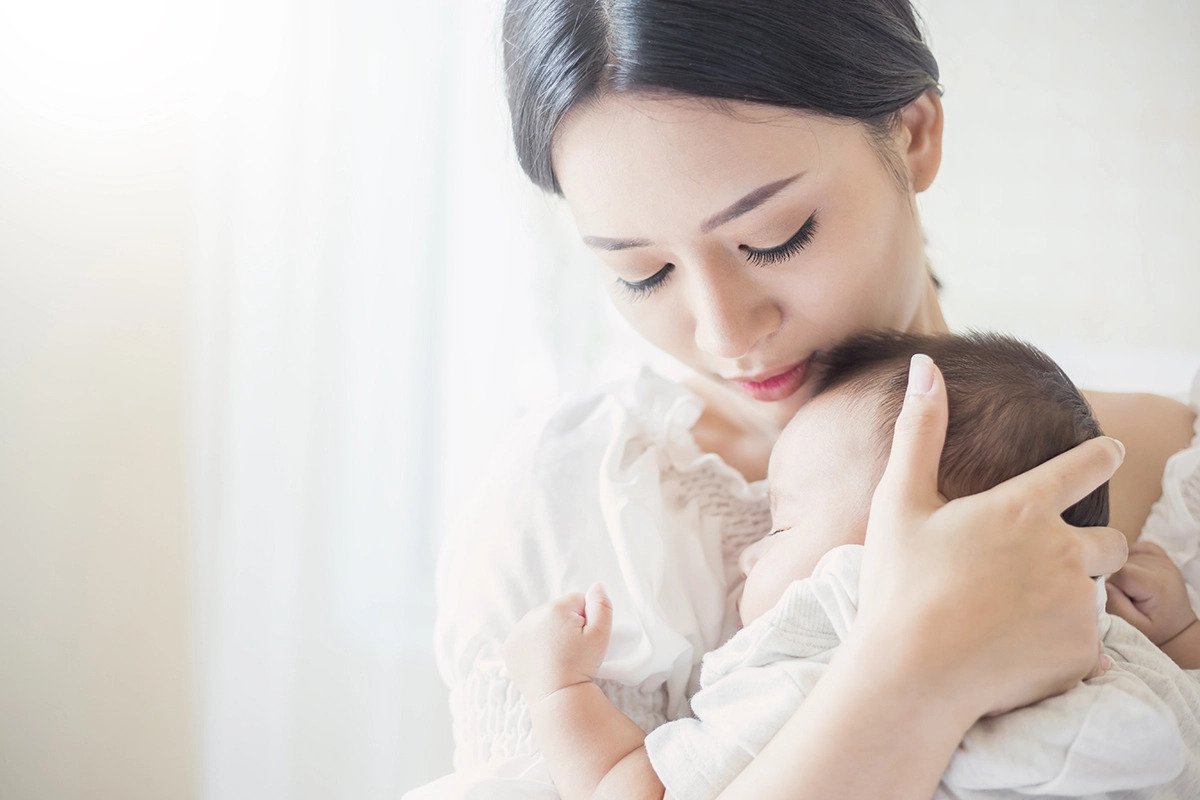
Cord blood banking may be
The best protection
for your baby
For only RM234 a month, you can have peace of mind against the unknown.

What is cord blood
Cord blood is the blood that remains in a baby’s umbilical cord and placenta after birth.

Lifesaving potential
Cord blood contains stem cells that can regenerate the blood and immune system.

Over 80 diseases
These cells have the potential to treat more than 80 disorders, such as leukaemia and lymphoma.

Family protection
Cord blood is a 100% match for your baby and has a higher chance of a match with her siblings.
Future potential
Cord blood is used in clinical trials for conditions such as autism, cerebral palsy and brain injuries.
Treat over 80 diseases
with cord blood stem cells
It is estimated over 85,000 cord blood units have been used to treat different diseases worldwide such as leukaemia, lymphoma and blood disorders.¹ Cord blood stem cell transplants are currently being used as standard mainstream treatment for the diseases listed here.
Diseases that can potentially be treated with cord blood stem cells
- Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
- Neuroblastoma
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Retinoblastoma
- Severe combined immune deficiency
- Multiple myeloma
- Aplastic anaemia
- Fanconi’s anaemia
- Congenital dyserythropoietic anaemia
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Thalassaemia major
- Osteopetrosis
Ongoing clinical trials using stem cells that can be found in cord blood
- Autism
- Cerebral palsy
- Global developmental
- Parkinson’s disease
- Spinal cord injury
- Stroke
- Myocardial infarction
- Alopecia areata
- Diabetes (Type 1 & 2)
- Lupus
- Multiple sclerosis
- HIV
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Cartilage injury
- Osteoarthritis
Over 3,000 clinical trials registered
Ongoing worldwide research is pushing science to discover the greater potential of stem cells that can also be found in cord blood. By storing your baby's umbilical cord stem cells, you are availing your family to more medical options in the future.
Reference: Clinicaltrials.gov. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=haematopoietic+stem+cells&Search=Apply&recrs=b&recrs=a&recrs=f&recrs=d&recrs=e&age_v=&gndr=&type=&rslt=. Accessed March 7, 2023.
More reasons to consider cord blood banking

Likelihood of
needing stem cells
We become more vulnerable to diseases as we age. Research shows that 1 in 3 people will benefit from regenerative medicine therapy.²
Higher chance
of finding a match
You're more likely to find a matched cord blood unit within the family than in the public domain for an available, suitably matched bone marrow donor. This means your family member can get treatment sooner.³
Lower risk
of complications
Studies have shown that transplant complications are lower when patients get stem cells from a family member.

Once-in-a-lifetime opportunity
You only have one chance to collect your baby’s precious cord blood: at birth. Once missed, this opportunity is lost forever.
- Cord Blood Utilization is Booming in China. Parent's Guide to Cord Blood Foundation. https://parentsguidecordblood.org/en/news/cord-blood-utilization-booming-china. Accessed March 5, 2024.
- Harris DT. Cord blood stem cells: a review of potential neurological applications. Stem Cell Reviews. 2008; 4:269-274.
- Gluckman E, Rocha V, Boyer-Chanmard A, et al. Outcome of Cord-Blood Transplantation from Related and Unrelated Donors. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337-373-381.

Access to
potential medical resource
Get a peace of mind knowing that you’ve given your family immediate access to a potential medical resource in case it’s ever needed.
How StemLife clients have benefited from their cryopreserved cord blood

StemLife has successfully helped our clients release their cryopreserved cord blood units for transplantation or therapy at 18 healthcare institutions in 9 countries









What diseases did our clients use cord blood to treat with?
Autologous
During an autologous transplant or infusion, the patient’s own stem cells are reintroduced into the body.
- Cerebral palsy
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Neuroblastoma
- Brain injury
- Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Global developmental delay
- Development dyspraxia
Allogeneic
During an allogeneic transplant or infusion, the patient receives stem cells from a donor.
- Thalassaemia major
- Aplastic anaemia
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Severe-combined immune deficiency

Most of them used their own cord blood
Most of the cord blood units released at the request of our clients were used on the child himself/herself, while the remaining units were used by the child's sibling.
Save your baby's cord blood now
to give your child access to his/ her own stem cells.
Cryopreserved exclusively for your own family
Your baby’s cord blood will be kept solely for your family, and we will conduct regular checks to ensure that it remains in good condition throughout the storage period.
Retrieve whenever you need
In the event that your baby's cord blood unit is required for a treatment, we will deliver it to any hospital within Malaysia at no extra cost. For treatments conducted overseas, we’ll work with a qualified partner to deliver your child's cord blood unit safely.
Holistic protection from pregnancy to adulthood
All clients gain access to our holistic protection through StemLife Advantage. This includes coverage for stem cell transplantation and other unforeseen circumstances that may arise.

SLB/PM-095/Rev00