Cord blood and cord lining banking
You may have heard, seen or read about cord blood and cord lining banking either through internet search, social media, leaflets at the clinics or even during your prenatal check-ups. Even your parents may have shared it with you at some point. That being said, do you know what exactly is cord blood and cord lining and for what purpose we bank them?
What is cord blood and cord lining¹?
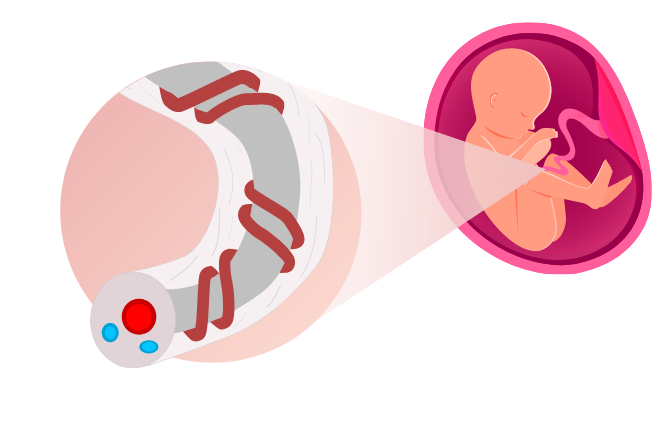
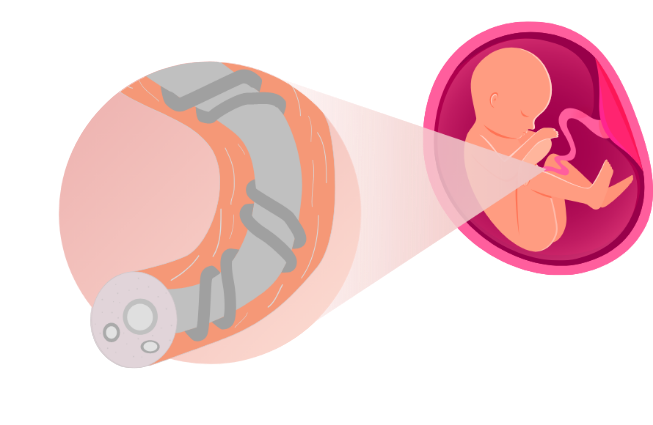
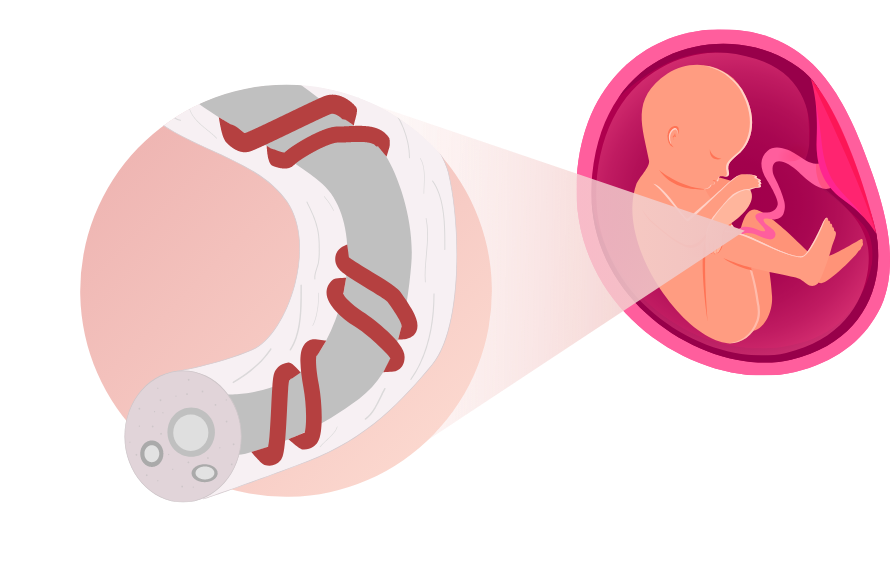
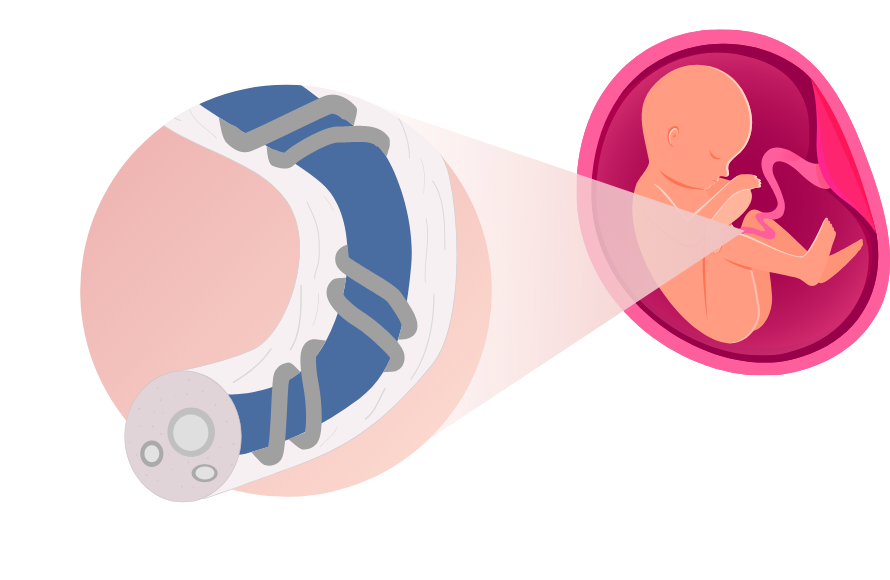
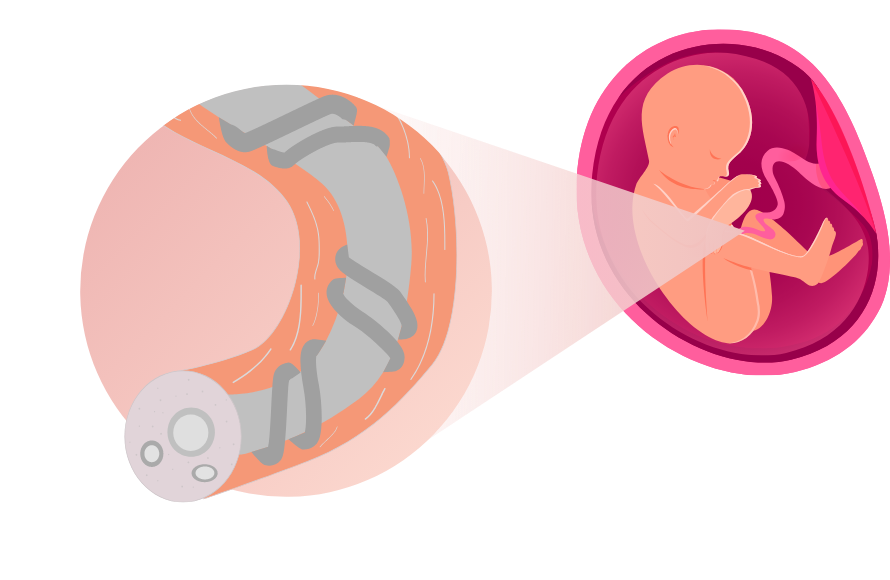
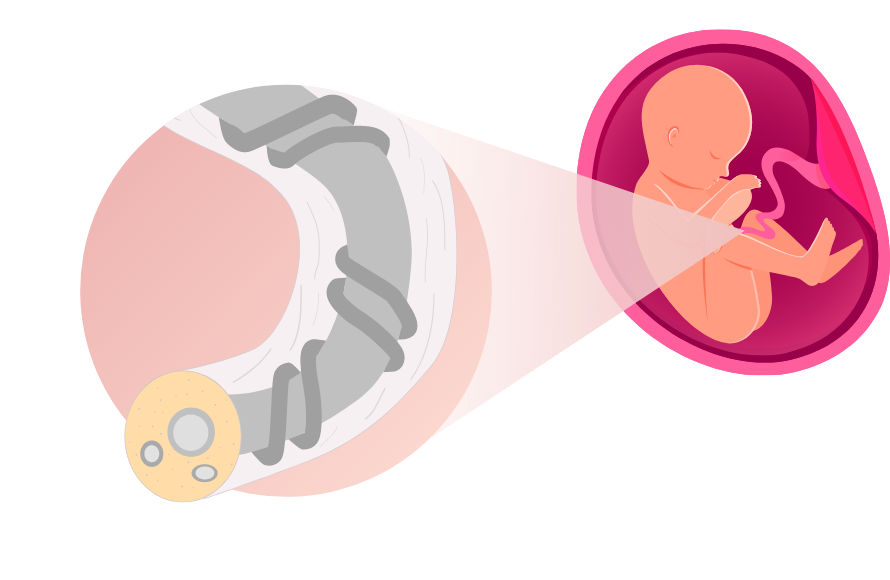
The umbilical cord is the tube-like structure that acts as a lifeline between the mother and the baby. It keeps the baby healthy by assisting in the nutrients and oxygen transport to the baby, while removing the baby’s waste product.
Cord blood
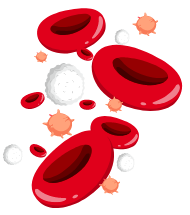
Cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord and placenta following the baby’s birth. It is a rich source of Haematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs), also known as blood forming stem cells. These stem cells can basically form into any type of blood cells in the body.
Cord lining
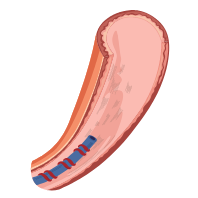
Cord lining is the protective layer that protects the internal components of the umbilical cord. Cord lining is a rich source of two other highly potent stem cells which are Cord Lining Epithelial Stem Cells (CLEpSCs) and Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
What is cord blood and cord lining
The umbilical cord is the tube-like structure that acts as a lifeline between the mother and the baby. It keeps the baby healthy by assisting in the nutrients and oxygen transport to the baby, while removing the baby’s waste product.
Cord blood
Cord blood is the blood that remains in the umbilical cord and placenta following the baby’s birth. It is a rich source of Haematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs), also known as blood forming stem cells. These stem cells can basically form into any type of blood cells in the body.
Cord lining
Cord lining is the protective layer that protects the internal components of the umbilical cord. Cord lining is a rich source of two other highly potent stem cells which are Cord Lining Epithelial Stem Cells (CLEpSCs) and Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
Understanding parts of umbilical cord
4 Things you need to know
about cord blood and cord lining banking

Readily available for you and your family
Cord blood and cord lining banking is an informed decision made to preserve your baby’s umbilical cord blood stem cells at temperature less than -150°c in the cryo tank for future use should your child her/himself or your family needs it. It can be done through private facilities. Having your cord blood and/or cord lining stored at a private facility will guarantee you a readily available cord blood unit containing precious and highly potent stem cells that can be used for you and your family. It keeps your mind at peace.
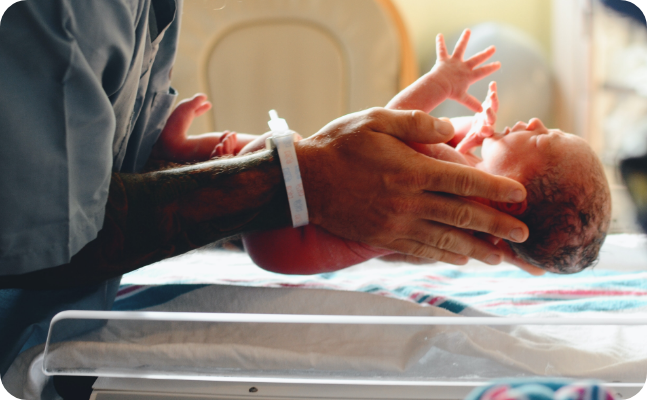

Safe, painless and easy
Cord blood collection can be done right after your baby’s birth where the doctor will clamp and cut the umbilical cord. The blood is then taken from the cut umbilical cord and the process only takes a few minutes. If you are storing cord lining, a portion of the umbilical cord that was cut, will be put into a sterile container and further processed for cryopreservation.
The collection process does not harm the mother or the baby nor will it disrupt the birthing process.
Cord blood - Used for over 80 types of diseases1,2
Cord blood is rich in HSCs which can develop into any type of blood cells like red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets.
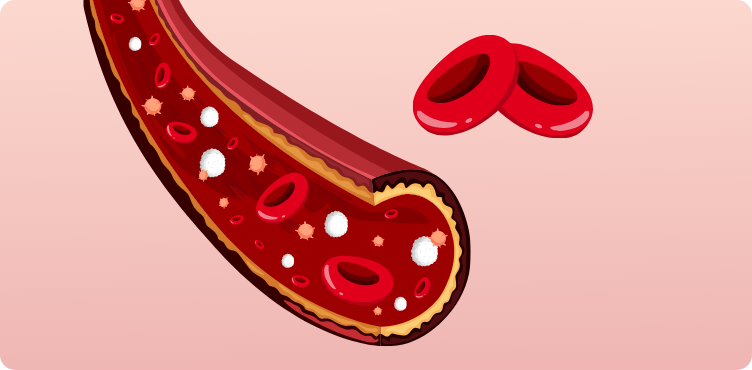
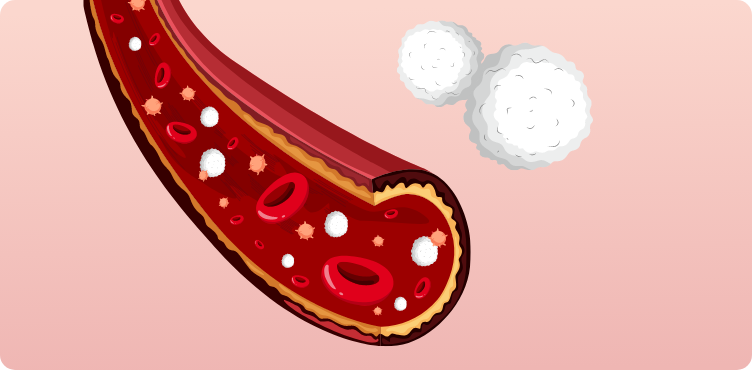
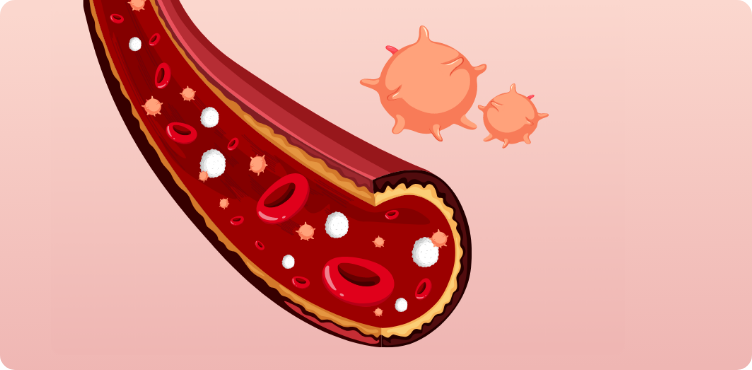
Cord blood stem cells can potentially:

Replace and regenerate damaged or diseased bone marrow

Treat blood cancers

Correct genetic defects (sibling/ allogeneic transplantation)

Potential to be used for cellular therapy and regenerative medicine
Cord Lining - Additional protection with promising medical potentials²
Cord lining contains both Cord Lining Epithelial Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cells.
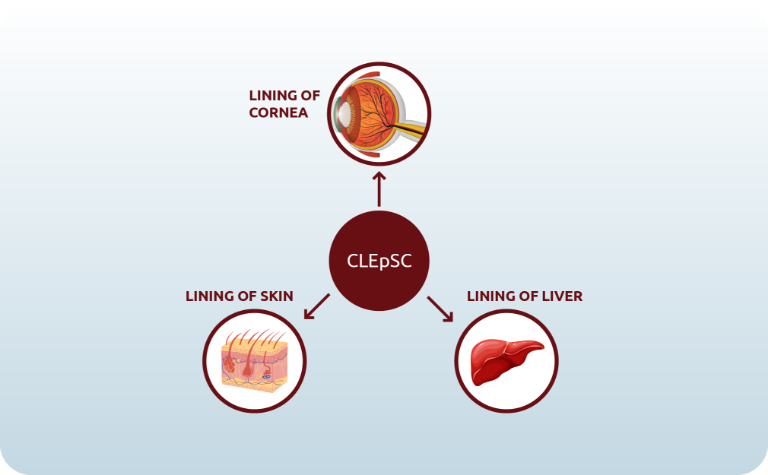
Cord Lining Epithelial Stem Cells (CLEpSC) form the soft tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body including cornea, skin, and liver.
CLEpSCs are important because they can differentiate into:
- Skin Cells
- Cornea Cells
- Liver Cells
- Insulin producing Cells
- Mucin producing Cells
- Inner Ear Cells
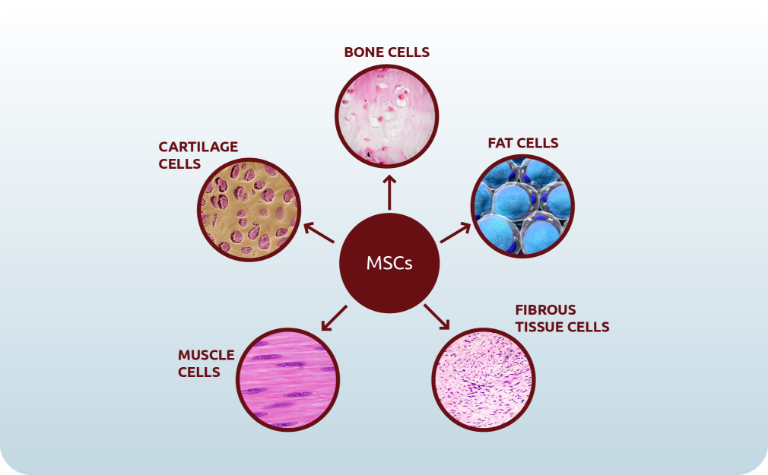
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) are the building blocks of structural tissues of our body such as bone, cartilage, muscle, fibrous tissues and fat and can potentially aid in the repair of injured tissues and organs.
MSCs are important because they can differentiate into:
- Fat Cells
- Cartilage Cells
- Nerve Cells
- Heart Cells
- Bone Cells

There are more than 1,000 clinical studies that are being conducted for MSCs obtained from the umbilical cord for the treatment of a variety of conditions.
Storing both cord blood and cord lining will give you more types of stem cells. You are availing your child to a medical advancement with access to a growing number of applications of stem cells and the therapeutic potential that they hold.
Fact:
Did you know that cord blood can be cryopreserved for decades?³
Storing both cord blood and cord lining will give you access to a wider variety of stem cells. You are providing your child and family with the opportunity to benefit from medical advancements, gaining access to an increasing number of applications of stem cells and the therapeutic potential they offer.




